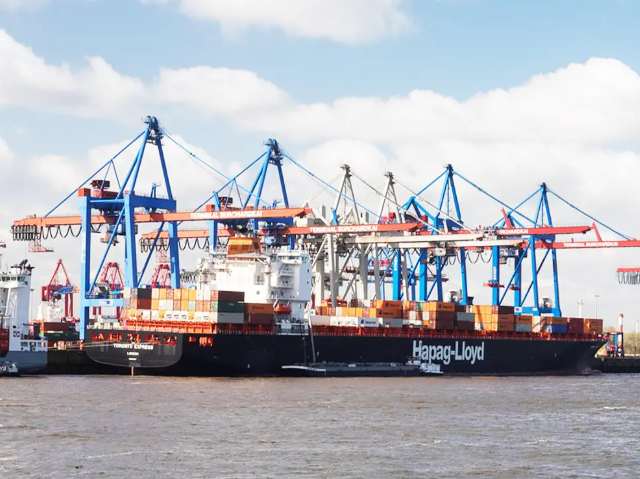
Core Components of Global Freight Forwarders' Cost Structures
Base Freight Rates: The Foundation of Shipping Costs
Freight rates form the foundation of what companies pay to ship goods around the world. A bunch of things affect these basic rates including how far something needs to go, which mode of transport gets picked (land, sea or air), and who actually handles the transportation job. Getting familiar with how these base prices vary from one shipping route to another really helps businesses plan their budgets better. Take major trade lanes for example they usually come with lower costs than those offbeat routes nobody travels much. Smart shippers know that talking about base rates during busy seasons when lots of cargo is moving makes all the difference in saving money. Rates jump through the roof during peak times like holidays, so knowing when to strike deals matters a lot in keeping shipping expenses under control.
How Volume and Weight Impact Global Freight Pricing
When it comes to shipping freight around the world, most companies calculate costs based on something called dimensional weight pricing. Basically, this means they compare how much space a package takes up versus what it actually weighs. So if someone ships something big but light like foam products, they'll probably pay more than for heavy metal parts that take up less room. Different freight companies have their own ways of calculating prices based on size and weight combinations, which explains why similar shipments can sometimes cost completely different amounts. Smart businesses try to cut down on these extra charges by thinking carefully about how they pack things. Making sure boxes aren't too empty or oversized helps align with those tricky weight and volume calculations. A little bit of packaging planning goes a long way toward keeping shipping bills from getting out of hand.
Seasonal Rate Fluctuations in Key Trade Lanes
Shipping costs tend to go up and down throughout the year, usually following busy times like holiday shopping sprees, summer vacation months, and big sales events such as Black Friday in November or Chinese New Year celebrations across Asia. Knowing when these price swings happen helps companies save money on transportation expenses. Looking at past data about how much rates change allows businesses to schedule deliveries when prices are lower instead of getting hit with higher charges during rush periods. Companies that track what's happening in major shipping routes gain an edge over competitors because they can better manage budgets and actually find windows where shipping gets cheaper rather than paying premium prices all the time.
Accessorial Charges in International Shipping
Fuel Surcharges (BAF) and Environmental Fees
Fuel surcharges, sometimes called Bunker Adjustment Factors or just BAFs, really affect how much companies pay for shipping goods around the world. When fuel prices go up and down, carriers calculate these extra charges as a percentage added onto regular freight rates. And lately there's been this growing trend of environmental fees too. Governments keep tightening regulations while companies try harder to cut down their carbon footprints. For anyone running a business today, knowing how these fuel adjustments and green taxes work matters a lot when budgeting for logistics costs and staying compliant with rules. These factors play a big role in global shipping prices because they tend to spike suddenly and send shipping bills through the roof without warning.
General Rate Increases (GRI) Explained
General Rate Increases, or GRIs, happen when carriers adjust their pricing to match what's going on in the market right now plus cover their own running expenses. When these hikes come through, they hit freight budgets hard and throw a wrench into operational plans, so companies really need to keep track of when carriers announce them. Looking at how different carriers behave with their rate changes helps businesses plan ahead sometimes even getting better deals at谈判 time. The truth is, GRIs just show how unpredictable the shipping world has become lately. Companies that want to survive economically have no choice but to roll with these constant price waves and adjust their strategies accordingly as markets shift month after month.
Security Fees and Port Congestion Add-ons
Security charges cover the expenses needed to meet those tough safety rules that became standard after 9/11. Port congestion charges pop up when there are delays at terminals caused by too much traffic or unexpected problems, so companies need backup plans ready. These extra costs show just how complicated international shipping really gets when delays happen and money starts piling up fast. Keeping lines open with freight forwarders about these extra charges helps manage budgets better and prepares businesses for surprise fee increases. Getting familiar with all these different charges makes a big difference when trying to handle the daily headaches of moving goods around the world.
Origin and Destination Service Fees
Customs Brokerage and Documentation Charges
Paying customs brokerage fees helps companies deal with all those complicated rules when moving stuff across borders. Without proper payment, shipments might get stuck at ports while officials check everything over again. The money covers making sure packages meet all the paperwork requirements too. Documentation charges pay for creating all those forms needed before goods can actually move from one country to another. For anyone running an import business, finding good customs brokers really matters because mistakes here cost time and money. We've seen plenty of cases where businesses paid extra fees later on just because their broker missed something simple on the paperwork side of things.
Drayage Costs for First/Last Mile Connections
Drayage plays a key role in supply chains when moving goods short distances typically from ports to nearby warehouses or distribution centers. Costs vary quite a bit based on several things including how far needs to be driven, whether trucks can easily get to loading docks, and just how heavy those containers actually are. Planning ahead really helps keep budgets on track. Companies that negotiate well with their drayage partners often see real savings while getting dependable service too. Good relationships matter here since timely pickups and deliveries make all the difference for keeping operations running smoothly across those critical first and last legs of any shipment journey.
Warehousing Fees and Cross-Docking Services
Storage charges really eat into overall shipping expenses, particularly if items sit around for months on end. The amount companies pay depends largely on how long products stay put plus any special conditions needed for proper storage. Many businesses combat these rising costs by turning to cross docking services. This works because goods get sorted right away and shipped out without ever going into long term storage areas. Companies find this method helps them save money on their bottom line while making the whole supply chain easier to manage. When looking at ways to cut down on transport spending, warehouse alternatives and cross docking effectiveness should be evaluated carefully against what actually makes sense for day to day operations and bottom line goals.
Payment Terms and Credit Options
15-30 Day Credit Terms for Approved Clients
Setting up 30 day payment terms with freight forwarders gives businesses a real edge when it comes to managing money flow. Most shipping companies actually offer this kind of arrangement these days, which helps firms spread out their outgoing cash without breaking the bank all at once. When companies stick to making those payments on time though, they build trust with their freight partners. This trust often opens doors for better pricing deals down the road. The bottom line? Getting familiar with these credit options makes sense for anyone looking to cut down on operational expenses while keeping their finances in good shape over the long haul.
Dynamic Pricing vs Fixed Validity Quotes
Freight service pricing that changes with market conditions offers companies flexibility they just don't get with fixed rate models. When fuel costs spike or demand drops off, these variable rates can actually save money over time. Smart businesses study both options carefully before making choices about how they source goods. Some companies track shipping indexes daily while others prefer the stability of locked-in rates for certain routes. Looking at historical data helps determine if going with dynamic pricing makes sense now versus later. Most logistics managers find themselves somewhere in between, mixing approaches depending on what's happening in different parts of the world supply chain.
Early Payment Discount Strategies
Many freight forwarders give early payment discounts as a way to get businesses to handle their money better. Companies that take advantage of these deals usually save real money on their bottom line while freeing up cash for other expenses. Creating a solid plan around getting paid early brings financial perks and helps build stronger relationships with shipping partners over time. The companies that do this tend to negotiate better rates eventually, which matters a lot when trying to stay competitive in today's tough maritime shipping market where margins are thin and competition is fierce.
Strategies for Budgeting Global Freight Operations
Consolidated Shipments for Cost Efficiency
Combining multiple shipments has become a go to method for cutting down on shipping costs across global freight networks. When companies send bigger batches at one price point instead of smaller ones separately, they tend to spend way less overall on moving goods around. This works especially well for international shipping since those fees just keep piling up fast. Working closely with reliable logistics providers makes all the difference too many businesses have seen savings upwards of 30% simply by consolidating their cargo. Getting the timing right matters a lot though nobody wants delays messing up everything else. Proper coordination between warehouse schedules and carrier availability helps ensure smooth operations while keeping money in the bank. At the end of the day, smart shipment consolidation isn't just about saving dollars it actually streamlines how entire supply chains function from start to finish.
Peak Season Surcharge Protection Clauses
Including protection clauses in freight contracts makes sense when dealing with those pesky peak season surcharges that hit so many businesses hard. These clauses basically serve as insurance against those unexpected price jumps that happen when demand spikes in global shipping markets. Companies that get ahead of this game by negotiating these protections early on tend to save themselves from serious cash flow headaches later. Looking at past trends within their specific sector helps companies figure out when these peaks usually occur, which gives them leverage in contract talks. When businesses know what to expect, they're not caught off guard by those freight cost surprises, and their budgets stay on track instead of getting blown out of proportion during busy seasons.
Multi-Modal Contract Negotiation Tactics
Using mixed mode shipping gives companies more flexibility and can actually save money when combining different transport options. For manufacturers and retailers especially, this kind of approach makes sense when looking at overall logistics costs. When it comes time to negotiate those shipping contracts, smart businesses build in some wiggle room so they can switch between rail, truck, or sea transport depending on what's cheapest at the moment. The real value here goes beyond just cutting expenses. Companies that properly evaluate multimodal shipping see better service delivery too. Most supply chain managers know that mixing road, air, and sea freight creates a smoother operation that adapts to changing conditions without breaking the bank. With fuel prices fluctuating all over the place lately and port delays becoming more common, having backup transportation plans isn't just good practice anymore it's practically necessary for staying ahead in today's fast moving freight environment.
Emerging Trends in Global Freight Pricing Models
Digital Freight Platforms and Real-Time Bidding
The rise of digital freight platforms has completely changed how logistics works in recent years. These online marketplaces let businesses compare prices and services from different carriers all in one place, which saves time and makes things run smoother. Real time bidding has become pretty common on most platforms too. This creates competition among providers and often leads to lower shipping costs for companies. When businesses switch to these digital tools, they typically see improvements in both speed and reliability of their supply chains while cutting expenses at the same time. For logistics managers looking to stay competitive today, getting familiar with these platforms isn't just helpful it's becoming something of a necessity if efficiency remains a top priority.
Sustainability Surcharges for Green Logistics
The extra fees called sustainability surcharges basically cover what it costs to run logistics operations in an eco-friendly way, and lately we've seen these show up more often on invoices. Companies need to get familiar with what these charges actually mean and figure out if they make sense compared to the green promises made in marketing materials. When dealing with all things green in supply chains, having some idea about how these surcharge amounts might go up and down helps managers plan budgets better and stay within those pesky environmental regulations everyone keeps talking about. Going green isn't just good PR either; real money gets saved when transport companies switch to cleaner fuels or optimize routes. Plus, customers notice when businesses walk the talk on sustainability issues rather than just making empty claims during board meetings.
Blockchain-Based Transparent Pricing Systems
The freight industry is seeing major changes in how prices get set thanks to blockchain tech. This new approach brings better accuracy when it comes to knowing exactly what things cost across the supply chain. When companies get their heads around how blockchain works in freight pricing, they start making smarter deals with suppliers and customers alike. The way pricing models are changing opens doors for some pretty cool innovations down the road. With blockchain's tamper-proof record keeping, everyone involved gets a clear picture of every transaction from start to finish. Freight shipping around the world is getting digitized fast these days. Going with blockchain systems makes sense if companies want pricing that's not only clearer but also runs smoother day after day. This matters a lot in today's complicated logistics landscape where small savings can make big differences in the bottom line.
How to Evaluate Global Freight Forwarder Cost Proposals
Comparing All-In vs Itemized Pricing Models
When deciding between all-in pricing versus itemized pricing in freight forwarding operations, companies need to think carefully about what works best for their bottom line. All-in pricing makes things simple at first glance since it bundles everything together into one neat package. But there's often a catch here too many hidden charges tend to pop up later that nobody expected when making those initial budget projections. Itemized pricing tells a different story altogether. With this approach, every penny gets broken down into specific categories so business owners can actually see where their money goes. Some find this level of detail overwhelming while others appreciate being able to track exactly how much they spend on fuel surcharges versus storage fees. Looking at both options side by side helps organizations pick whichever matches their long term financial goals better. Knowing precisely what comes included in each pricing model remains essential for anyone trying to manage cash flow effectively without any nasty surprises down the road.
Validating Fuel Calculation Methodologies
Getting a handle on how freight forwarders calculate fuel charges matters a lot if companies want to avoid getting charged extra. The truth is fuel prices go up and down all the time, which really affects what gets charged for shipping goods. Companies need to know exactly how those price changes get translated into actual numbers on invoices. Looking at fuel charges regularly through audits helps keep costs in check and makes sure what's being paid matches what's happening in the market. When businesses actually check these calculation methods instead of just trusting them blindly, they save money in the long run and stop those surprise bills that come out of nowhere and mess with budgets.
Service-Level Agreement (SLA) Cost Guarantees
Service Level Agreements or SLAs basically set the ground rules for what to expect from freight services and how much they'll cost. These agreements make it clear who is responsible for what, listing out exactly which services come with which price tags. When companies stick to SLA terms, they avoid those nasty surprises where costs suddenly balloon out of nowhere. This helps keep budgets stable because everyone knows what to expect upfront. Getting these agreements right means making sure they actually match what happens in real life, not just some ideal scenario. Good SLAs should also cover those unexpected situations that always seem to pop up. For businesses dealing with freight day in and day out, having solid SLAs in place creates order in an otherwise chaotic process while keeping carriers honest about their commitments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are base freight rates?
Base freight rates are essential shipping costs determined by various factors such as distance, shipping method, and carrier choice.
How do volume and weight affect freight pricing?
Freight pricing can be influenced by dimensional weight pricing, which compares the volumetric weight to the actual weight of goods.
What are fuel surcharges?
Fuel surcharges, also known as Bunker Adjustment Factors, are additional fees calculated based on fluctuating fuel prices.
How can businesses benefit from credit terms with freight forwarders?
15-30 day credit terms allow businesses to improve cash flow management and negotiate better rates with freight forwarders.
What is the impact of sustainability surcharges?
Sustainability surcharges account for costs associated with green logistics practices, reflecting a business's commitment to eco-friendly processes.
Table of Contents
-
Core Components of Global Freight Forwarders' Cost Structures
- Base Freight Rates: The Foundation of Shipping Costs
- How Volume and Weight Impact Global Freight Pricing
- Seasonal Rate Fluctuations in Key Trade Lanes
- Accessorial Charges in International Shipping
- Fuel Surcharges (BAF) and Environmental Fees
- General Rate Increases (GRI) Explained
- Security Fees and Port Congestion Add-ons
- Origin and Destination Service Fees
- Customs Brokerage and Documentation Charges
- Drayage Costs for First/Last Mile Connections
- Warehousing Fees and Cross-Docking Services
- Payment Terms and Credit Options
- 15-30 Day Credit Terms for Approved Clients
- Dynamic Pricing vs Fixed Validity Quotes
- Early Payment Discount Strategies
- Strategies for Budgeting Global Freight Operations
- Consolidated Shipments for Cost Efficiency
- Peak Season Surcharge Protection Clauses
- Multi-Modal Contract Negotiation Tactics
- Emerging Trends in Global Freight Pricing Models
- Digital Freight Platforms and Real-Time Bidding
- Sustainability Surcharges for Green Logistics
- Blockchain-Based Transparent Pricing Systems
- How to Evaluate Global Freight Forwarder Cost Proposals
- Comparing All-In vs Itemized Pricing Models
- Validating Fuel Calculation Methodologies
- Service-Level Agreement (SLA) Cost Guarantees
- Frequently Asked Questions


